Open Innovation is the process of innovation that revolves around the free flow of ideas, in search of business solutions across corporate boundaries, from partnerships with other organizations and research institutions.
1. What is Open Innovation?
Innovation is the key for companies from different segments to stay up-to-date and competitive in their areas of expertise. In the world of Digital Transformation, with competition just a click away, being ahead of the market is no longer a matter of cutting edge and has become a business strategy.
Traditionally, the search for innovation happens internally, with the organization’s own teams seeking the development of new products and services, or the improvement of those already existing. The problem is that this type of initiative requires large investments in research, in addition to hiring highly qualified professionals.
So how can a company stay attractive and competitive to consumers by offering innovative products and services without the high added costs?
Open Innovation enables industries and companies to promote open ideas, research and processes to increase productivity and efficiency, enhancing product development and optimizing the services offered.
This external collaboration allows the development in a decentralized way, by professionals who may be distant geographically, but approach and act in the same challenge, through the internet.
In Open Innovation, the expertise and knowledge needed to solve a specific business challenge, usually fostered in closed research and development centers, is obtained through partnerships with other companies or technology institutions.
In practice, it means that Open Innovation allows for the encounter between the company that has a business challenge and the professionals, research institutions or partner companies that have already developed the technology needed for its solution – or are in the process of developing it.
This business strategy is also capable of providing a broader view of what the market has been developing, with a focus on new ideas.
Open Innovation is a perception that corporate research and development centers are no longer able to generate all the innovations at the speed and intensity necessary for the company to remain relevant in the market. Thus, you can find innovations that are ready – and can already be implemented – or search for players who are better positioned in certain areas.
It is important to emphasize that this external collaboration can have as a counterpart a commercial relationship. Who defines the bases of the partnership are the companies and institutions involved in the process.
Subscribe to receive our updates
Fill the form to receive our freshest content
2. What is Open Innovation for?
The practices of Open Innovation enable the reduction costs through hiring of specialized professionals, looking externally for the expertise necessary to the proposed challenges. It also accelerates time-to-market (time it takes to reach the market), increasing profitability and generating profit for organizations in different markets.
Open Innovation also reduces possible risks in innovation projects, significantly increasing the chances of success. The process can be applied in different contexts and markets, and is not restricted to the corporate environment, making it possible to incorporate it into political, social, artistic, and other scenarios.
3. Open Innovation: why is it important for your business?
Open Innovation reduces the costs of developing or improving products and services, increases competitiveness through differentiation in the marketplace, creates new revenue for the company through agility and objectivity, and reduces the time between the birth of ideas and their arrival to the market.
By expanding innovation practices beyond corporate boundaries, companies not only reduce their costs with innovation, but gain new ways of thinking about their business strategies, with an out-of-company view: more airy, objective and without the issues organizational culture may carry. Bringing the eye of external collaborators to the company provides a constant and invigorating flow in the innovation process.
The practices of Open Innovation presuppose the search for innovation beyond the limits of the organization and the development of solutions in a decentralized manner. The key benefits of this process for the company seeking answers to their business challenges in collaboration are:
COST REDUCTION
The company does not have to face the high costs of captive research and development centers or the hiring of highly qualified professionals in the quest for punctual solutions.
TIME-TO-MARKET REDUCTION
Reduce time to market, that is, the timeframe between generating ideas to solve the business challenge and the shelf.
MORE FLEXIBILITY
Through collaboration with better positioned players in relation to a new trend, the company can adapt to market changes.
NEW OPPORTUNITIES
Through collaboration with more active and well-positioned companies and institutions, it is possible to explore new market segments
GENERATION OF NEW BUSINESS
The products generated internally and that will not be exploited by the company, for different reasons, can be marketed externally, through partnerships with institutions that are in a more propitious moment.
4. How is Open Innovation used in business?
We will use the automotive industry to exemplify how Open Innovation can be used by companies. Automakers have been suffering a significant impact due to changes in consumer behavior and the emergence of disruptive companies that offer alternative transportation models.
The arrival of Uber, which turned common cars into taxis, Tesla’s innovative proposal with its self-driven vehicles, and new user behavior – more conscious and focused on collaborative economy – could be seen as threats. However, they appear as a reinvention of the sector.
And the moment that could have turned into the great crisis of the automotive industry gave place to the adoption of initiatives of Open Innovation. Companies in this segment are the best examples of how the Open Innovation process can accelerate project development.
For example, in the production of increasingly intelligent cars, you need expertise that the company does not necessarily have at its disposal. In addition to the knowledge about the operation of modern automobiles, which automakers hold, there is a need for projects focused on data transmission, Artificial Intelligence, continuous information transfer, among other technologies. And the know-how to develop these solutions can be found outside the corporations.
These specific needs open space for Open Innovation initiatives, starting with partnerships with technology companies that already have the solutions developed and tested or can adapt what has already been created for a given industry.
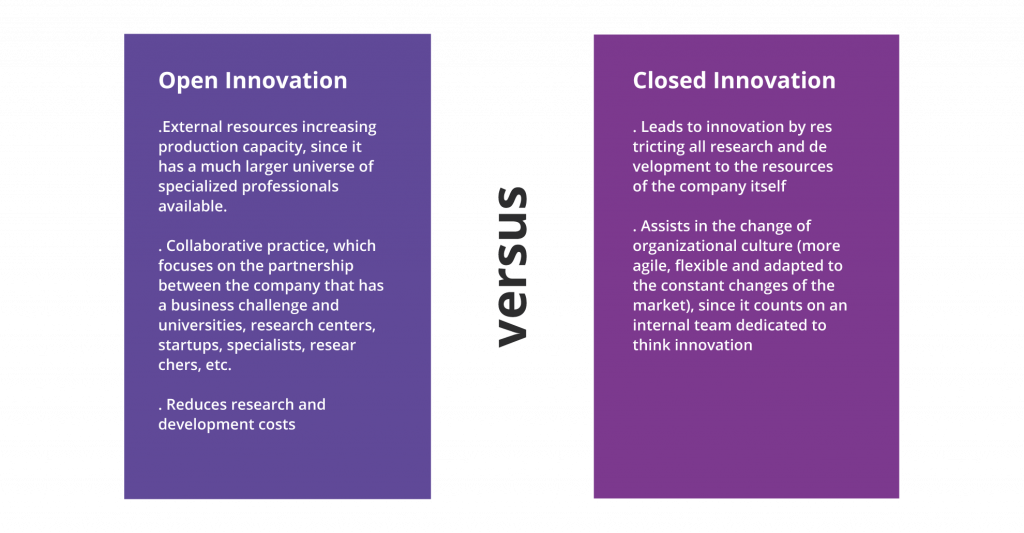
5. Open Innovation vs Closed Innovation: what’s the difference?
The differences between the practices of Open and Closed Innovation can be defined as:
6. Types of Open Innovation projects
There are 3 types of Open Innovation: Inbound Open Innovation, Outbound Open Innovation and Coupled Open Innovation. And they can be defined as follows:
This is the aspect of Open Innovation that happens when an organization adapts an innovation developed by other institutions, transforming and generating value for itself.
First, the company identifies the business challenge that will be worked on through external partnerships. After mapping and selecting the partners, they are invited to participate in the project in a collaborative manner.
Reasons for selecting partnerships include: organizations that have the expertise to develop the solution to the proposed challenge, better market positioning, availability of financial or human resources, ready-to-use technologies, and the possibility of adaptation – a favorable business model to achieve the project objective, appropriate facilities, such as labs, among others.
In the process of Outbound Open Innovation, a company develops an innovation and makes it available to external partners, in order to develop the solution or market it.
Companies that foster the Culture of Innovation internally often end up generating ideas that will not be developed for different reasons – inventions are not aligned with business strategy, it may not be a good moment due to cost, there is no internal expertise to transform the prototype in a marketable product or service, lack of distribution channels, among others.
In these cases, these inventions do not fall into the scope of result generation and end up being obsolete and unhelpful. Open Innovation practices allow these ideas to go off paper.
In the practices of Coupled Open Innovation, two or more companies come together to generate innovation, but each organization individually explores the resulting asset of this collaboration.
This format has been widely used to facilitate or make feasible the entry of companies that belong to the project into a new market and also projects with a high level of complexity.
A great example of this kind of approach has happened to the United States functional food industry. The strong regulation of the market by the FDA imposed strict rules on suppliers, such as the creation of research laboratories and high quality control, similar to what is already being applied to drugs. These changes would require large investments from the food industry, which had only one alternative: seek partnerships.
The formula they came up with that would not lead to them bringing and end to their activities, was to ally with the pharmaceutical industry, which already had the expertise and structure necessary to meet the expectations of the FDA. Thus, the merger between companies from completely different segments opened up the possibility of exploiting a new regulated market.
7. Methodologies for the application of Open Innovation
Different methodologies can support Open Innovation initiatives. These include:
Design Thinking
Design Thinking can be deployed to understand the end user. This approach aims to observe the behavior of the user, their needs and desires, generating empathy. Thus, it is possible to define the demand and propose assertive solutions, which will be prototyped and tested, before its implementation.
Lean Startup
Lean Startup is a set of processes that seeks to correctly test the innovations that have been developed. In this way, it is possible to sustain the hypotheses of innovation, without wasting time or money.
Hackathon
The hackathons bridge the gap between researchers, universities, experts and startups, with the goal of producing Open Innovation. Very common in Silicon Valley, prototyping marathons can accelerate innovation practices.
In meetings that last two days (usually on weekends), these professionals are challenged, and need to be overcome through co-creation. As a result, it is possible to get quick fixes to complex problems and maintain a bank of ideas for future projects. innovation.
Another advantage of hackathons is the impact on organizational culture, broadening the look on their own products and guiding internal teams to innovate in a more agile and objective way, through the development of prototypes.
Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing strategies such as site development, landing pages and campaigns to support Scouting initiatives, helping identify partners capable of developing solutions to specific challenges, among startups, researchers, etc.
Agile Sprints
Benefiting from all the benefits of agile methods, the solution is implemented in the company, taking into account the internal determinations of IT, corporate governance, among other variables.
Design Sprints
Ideal methodology to accompany the development of a short-term solution, based on a concrete market demand.
8. MJV’s Innovation Ecosystem
At MJV, the Innovation Ecosystem supports the three approaches to Open Innovation projects (Inbound, Outbound and Couple), from 4 main pillars:
Environment
Knowing that innovation projects are favored by an environment conducive to the generation and development of ideas, based on initiatives of co-creation, MJV created its Digital Transformation Laboratory, with emphasis on Open Innovation.
Located at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) – one of the most innovative universities in the country – the goal of the lab is to foster projects based on real market demands. The lab will act as an important hub between large companies, startups, SMEs and teaching and research centers of UFRJ, through its faculty, researchers and students, with a focus on developing new digital businesses.
Process
Based on collaborative innovation, MJV maintains its own process for managing the Innovation Ecosystem. An extension of Thinking Design, this approach has 6 steps:
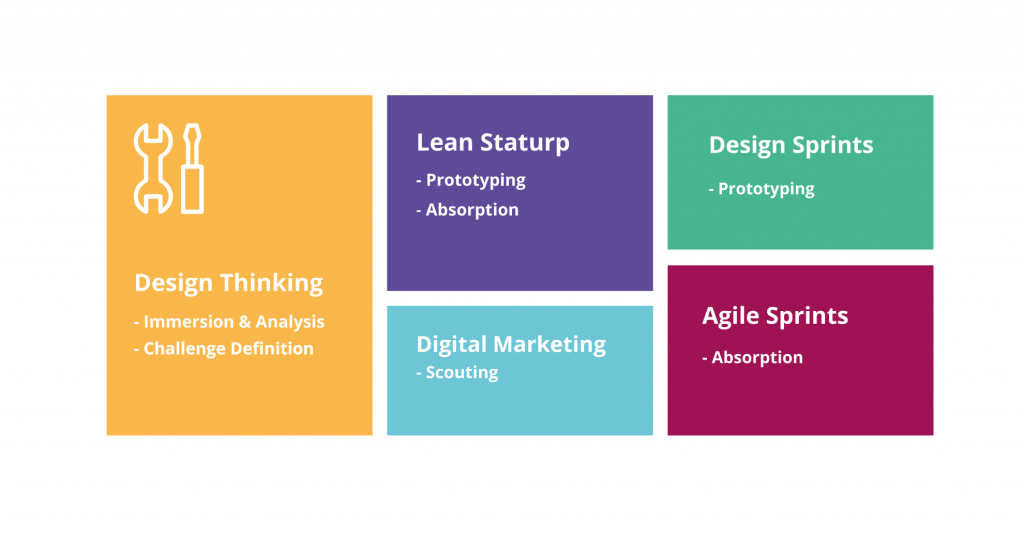
IMMERSION & ANALYSIS: Immersion process, with the identification of the real needs and opportunities of partnerships, from the approach of the context to the perspective of the different stakeholders
CHALLENGE DEFINITION: In this second step, the challenge to be addressed from Open Innovation initiatives is defined. At this stage we also select the participants and define a marketing campaign for attraction.
SCOUTING: Use of the own StartBusiness Community platform to attract specialists, organize events, disseminate in different communication channels and activate the partner base of UFRJ.
MATCHMAKING: Support to select partners, based on assessment information and mobilization of the execution team, organization of events to support the partnerships that best meet the business objectives of the contracting company.
INVENTION PROTOTYPING: This phase consists of actions of consulting and management of the executing team, with acculturation of executives, from innovative methodologies such as Design Thinking, Lean Startup and Agile.
INNOVATION ABSORPTION: Implementation of a pilot project on the contractor’s site, ensuring that internal processes are aligned with the proposed innovation.
Relationships
MJV maintains collaboration agreements and close relationship with UFRJ institutes, with the support of articulation of the Technological Park, ensuring the activation of this network of relationships, based on a specific demand.
And the numbers are impressive: UFRJ has a community of 52,000 people, including professors, researchers, students, technicians, employees and entrepreneurs, as well as 800 laboratories with different lines of research.
In addition to the excellent relationship with UFRJ’s research institutes, MJV also maintains an extensive network of professionals and corporations from different segments, which has:
. Database with 4 million specialists;
. Database with 6500 Brazilian startups;
. Database with 2.5 million business executives from around the world;
. 25,000 subscribers, who receive weekly free content on innovation produced by MJV experts.
Tools
Each step of the Open Innovation process demands a strategy to achieve the expected result. That is why the MJV makes use of different approaches, methodologies and tools, applying them in a specific and planned manner, in each of the stages.
The table below describes the different stages of the Open Innovation process in which the expertise are applied:
9. MJV’s Open Innovation Lab at UFRJ
In order to deliver even more quality in Open Innovation services, seeking solutions to complex challenges, MJV signed a contract with the UFRJ Technology Park, implementing in its place its newest Digital Transformation Lab, with an emphasis on Open Innovation.
Set up in a 360m² area, the Lab aims to promote an environment conducive to the generation and development of ideas, based on co-creation initiatives.
The Digital Transformation Lab
Address
R. Paulo Emídio Barbosa, 485, hangars 9 and 10 of the M.P. (Prototyping Modules)
Dimensions:
360m²
Hours:
9 am to 5 pm
Activities:
- Acceleration of startups
- Incubation of startups
- Co-working
- Development of Open Innovation projects
- Technical visits
- Events
- Promotion of entrepreneurial and innovative culture
- Pitches
The Lab aims to work on different fronts of Open Innovation. Among the available services are:
STARTBUSINESS COMMUNITY
Open Innovation Initiative developed by MJV that seeks to connect large companies and startups, through concrete demands for services, generating representative businesses for this ecosystem.
CORPORATE HACKATHON
A brilliant competition, designed to develop the best solutions to different challenges, fostering a culture of innovation in companies.
COCRIATION WITH EXPERTS
The co-creation process with experts focuses on:
. Enable the access of companies to a wide network of researchers and professors of UFRJ, in the search for solving business problems based on specific demands and technologies. This support is given through the structuring of the opportunity and the identification of professionals, with the mobilization of the University’s ecosystem.
. Structuring of teams of specialists, composed of professionals from MJV (Design Thinking and Technology) and experts (specific knowledge related to the theme of the challenge).
. Coordination of the MJV, with the implementation of projects and control of deadlines, costs and quality.
ACCELERATION OF STARTUPS
The startup acceleration is primarily aimed at leveraging promising business. Our acceleration advises the heads of the startups, supporting the consolidation of the idea and positioning in the market. The business model is cut to the point of transforming the project into something concrete and contributing, as a priority, to the demands of our clients.
CROWDSOURCING
At MJV, the crowdsourcing process is focused on supporting companies in structuring the business challenge and finding solutions to problems, through challenges proposed in a crowdsourcing platform, available to the network of students, professors and researchers at UFRJ. We also follow the actions, promoting involvement through network triggers and suggestions for adaptations in the program.
GROUNDBREAKER: OPEN INNOVATION PLATFORM
Developed by MJV, this is a simple and intuitive application that automates the process of Open Innovation through Gamification.
10. Open Innovation Trends
The future arrived and, with it, things that seemed unlikely, became a palpable reality. Fiat Chrysler Automobilis (FCA) has announced that it will provide units of its Pacifica minivan for the launch of Waymo’s unmanned cab service.
Waymo is Uber’s big competitor in the autonomous vehicles segment and is making a lot of moves within the industry. The company intends to provide its services in 25 American cities where the technology has already been tested, such as Atlanta, San Francisco and Detroit.
Instead of struggling with innovation, other leading names in the auto industry have also announced partnerships with Waymo. It has been made clear that companies do not need to spend years searching for solutions within their own sites if they adopt new technologies that have already been tested and approved.
This is the case of the British Jaguar, who joined Waymo to develop a completely autonomous version of I-Pace, its new luxury car model for driverless taxi services, which is already being tested.






